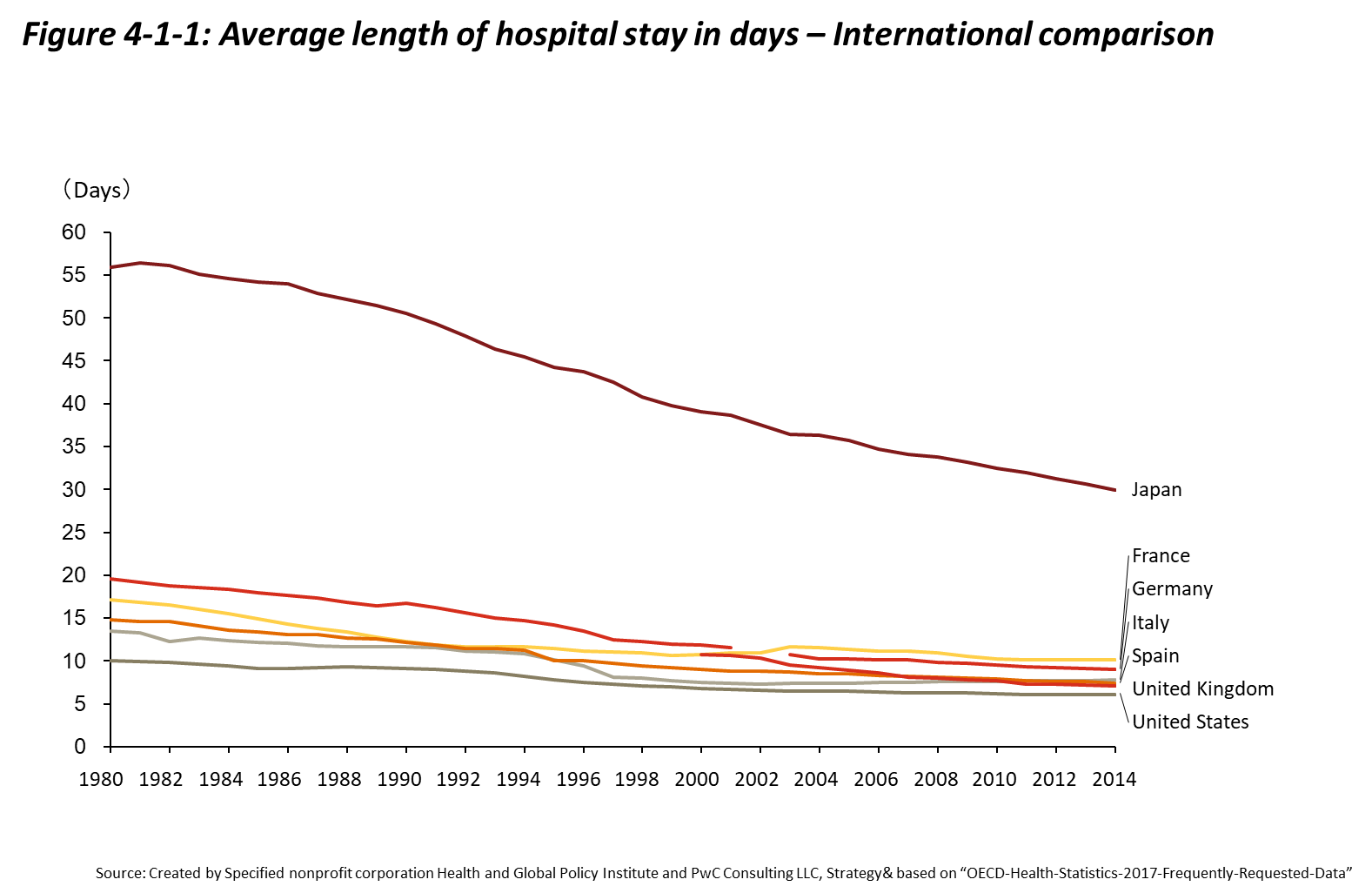
Under universal health coverage (UHC), and because Japan’s healthcare delivery system ensures unrestricted access, patients are able to receive care at any medical facility throughout the country. Another characteristic of Japan’s healthcare delivery system is that it is primarily managed by private organizations, with private hospitals (medical corporations) accounting for 70% of all hospitals and owning 50% of all hospital beds. When viewed from an international perspective, the number of hospital beds per capita in Japan is comparatively high, the average length of hospitalization is long, and the number of healthcare professionals per bed is low. For example, as shown in Figure 4-1-1, although the average length of hospitalization is falling, it remains long in comparison to other countries. On the other hand, it is important to recognize that simple comparisons are not possible, since the types of hospital beds used for calculations vary by country.[1]
4.1 Overview of Japan’s Healthcare Delivery System
References
[1] Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare “Current Situation and Issues Regarding the Healthcare Provision System” http://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/05-Shingikai-12601000-Seisakutoukatsukan-Sanjikanshitsu_Shakaihoshoutantou/0000184301.pdf (Accessed 2018, Feb.1)

