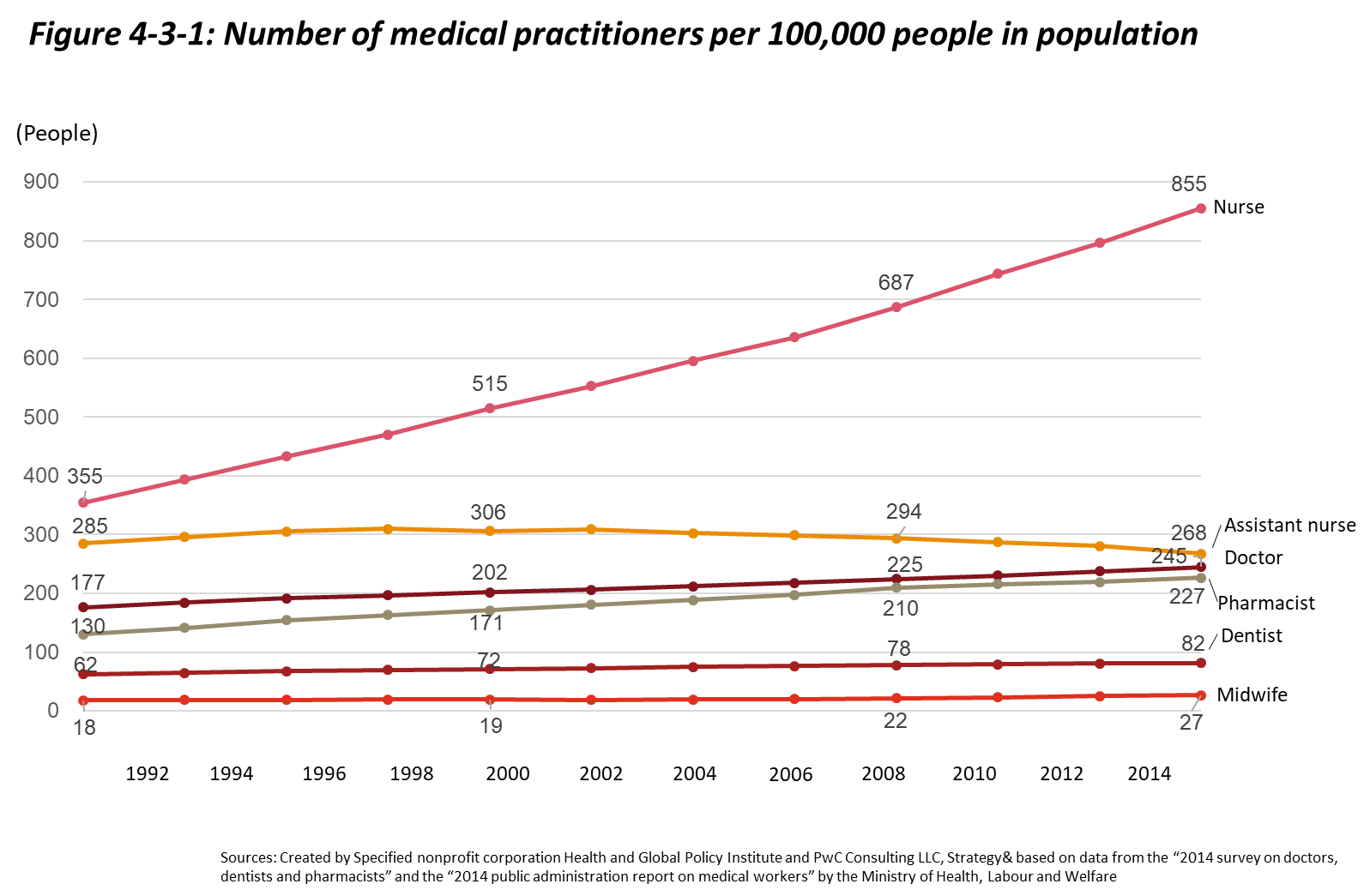
As shown in Figure 4-3-1, nurses are the fastest-growing category among medical professionals in Japan, while the number of doctors has remained relatively constant, only increasing by about 4,000 people per year.
4.3 Numbers of Medical Professionals
Although doctor shortages previously pointed out in obstetrics and general surgery have been in decline since 1994, regional maldistribution of doctors remains an issue, so a variety of actions are being undertaken. Specific examples include (1) supporting increases in university admissions by utilizing regional frameworks; (2) supporting regional medical support centers; (3) supporting clinical departments that suffer from shortages such as obstetrics and pediatrics; (4) supporting clinical training programs, (5) supporting a new system of medical specialists; and (6) organizing conferences to discuss the demands of medical practitioners. Regarding point (5), although implementation of the new medical specialist system was originally planned for FY2017, it was postponed until FY2018 due to concerns that the system might cause significant confusion in regional medical institutions.[7]
Concerning the new medical specialists system, which has been the subject of much debate related to the impact that it will have on regional healthcare in terms of the maldistribution of physicians, many have thus far expressed concerns about the consistency of accreditation standards for specialists under the independently managed academic institutions and the maintenance of physician quality. The new system has been constructed with the aim of improving that quality and providing high-quality medical care. Specifically, a framework has been established for appointing neutral, third-party organizations and for the consistent evaluation and certification of specialist accreditation and specialist development programs.[8]
References
[7] Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare “2. Physician Maldistribution Countermeasures” http://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/05-Shingikai-12601000-Seisakutoukatsukan-Sanjikanshitsu_Shakaihoshoutantou/0000184302.pdf (Accessed 2018, Feb.1)
[8] Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare “2. Physician Maldistribution Countermeasures” http://www.mhlw.go.jp/file/05-Shingikai-12601000-Seisakutoukatsukan-Sanjikanshitsu_Shakaihoshoutantou/0000184302.pdf (Accessed 2018, Feb.1)

